Write Objective-C Code
Write Objective-C Code
If you’re new to programming for iOS or Mac OS X, you need to become acquainted with the primary programming language, Objective-C. Objective-C is a not a difficult language, and once you spend some time with it you’ll appreciate its elegance. The Objective-C language enables sophisticated object-oriented programming. It extends the standard ANSI C programming language by providing syntax for defining classes and methods. It also promotes dynamic extension of classes and interfaces that any class can adopt.
If you are familiar with ANSI C, the following information should help you learn the basic syntax of Objective-C. And if you have programmed with other object-oriented languages, you’ll find that many of the traditional object-oriented concepts, such as encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism, are all present in Objective-C. If you are not familiar with ANSI C, we strongly encourage you to at least read an overview of the C language before you attempt to read this article.
The Objective-C language is fully explained in The Objective-C Programming Language.
About Objective-C
The Objective-C language specifies a syntax for defining classes and methods, as well as other constructs that promote dynamic extension of classes and adaptive interfaces.
A Superset of C
As a superset of the C programming language, Objective-C supports the same basic syntax as C. You get all of the familiar things, such as primitive types (int, float, and so on), structures, functions, pointers, and control-flow constructs such asif...else and for statements. You also have access to the standard C library routines, such as those declared instdlib.h and stdio.h.
Objective-C adds the following features to ANSI C:
-
Syntactical conventions for defining new classes
-
Conventions for class and instance methods
-
Syntax for method invocation (called messaging)
-
Syntax for declaring properties and synthesizing accessor methods from them
-
Conventions for static and dynamic typing
-
Blocks—encapsulated segments of code that can be executed at any time
-
Extensions to the base language such as protocols and categories
Don’t worry if these aspects of Objective-C are unfamiliar to you now. As you progress through the remainder of this article, you will learn about them. If you’re a procedural programmer new to object-oriented concepts, it might help at first to think of an object as essentially a structure with functions associated with it. This notion is not too far off the reality, particularly in terms of runtime implementation.
The Objective-C Advantage
In addition to providing most of the abstractions and mechanisms found in other object-oriented languages, Objective-C is a very dynamic language, and that dynamism is its greatest advantage. It is dynamic in that it permits an app’s behavior to be determined when it is running (that is, at runtime) rather than being fixed when the app is built. Thus the dynamism of Objective-C frees a program from compile-time and link-time constraints and shifts much of the responsibility for symbol resolution to runtime, when the user is in control. The dynamism of Objective-C springs from three sources:
-
Dynamic typing enables your code to determine the class of an object at runtime. The
iddata type makes it possible to substitute any type of object at runtime. You can thereby let runtime factors dictate what kind of object is to be used in your code. Dynamic typing thus gives your program much greater flexibility than static typing does, although with a tradeoff of less strict data integrity.Note: Static typing, in which the class type is specified (for example
NSString *var), has its benefits too and is, in fact, more commonly used than dynamic typing. For example, with static typing the compiler can fully analyze your code. And it brings better performance and predictability to your code. In other object-oriented languages, dynamic typing is sometimes called weak typing and static typing is called strong typing. -
Dynamic binding allows your code to determine the method to call at runtime instead of at compile-time. Just as dynamic typing defers the resolution of an object’s class membership until runtime, dynamic binding defers the decision of which method to invoke (or call) until runtime. Method invocations are not bound to code during compilation as with other object-oriented languages; they are bound only when a message is actually delivered.
With both dynamic typing and dynamic binding, runtime factors determine which receiver is chosen and which method is called. For example, a drawing program could define an assortment of graphical-shape classes inheriting from a common Shape ancestor class; you can invoke a
drawmethod on an object without having to know in advance the object’s class and how it will draw itself. -
Dynamic loading allows your program to add modules of code and other resources at runtime. With dynamic loading, an application can load executable code and resources as they’re needed instead of having to load all program components at launch time. This capability enhances performance. The executable code can contain new classes that are integrated with the runtime image of the program.
Classes and Objects
As in most other object-oriented languages, classes in Objective-C support encapsulating data and defining the actions that operate on that data. An object is a runtime instance of a class and contains its own in-memory copy of the instance variables declared by that class and pointers to the methods of the class. You create an object in a two-step procedure called allocation and initialization.
The specification of a class in Objective-C requires two distinct pieces: the interface and the implementation. The interface portion contains the class declaration and defines the instance variables and methods associated with the class. As with C code, you define header files and source files to separate public declarations from the implementation details of your code. (You can put other declarations in your implementation file if they are part of the public programmatic interfaces.) These files have the filename extensions listed in the following table.
|
Extension |
Source type |
|---|---|
|
|
Header files. Header files contain class, type, function, and constant declarations. |
|
|
Source files. A source file with this extension can contain both Objective-C and C code. |
|
|
Source files. A source file with this extension can contain C++ code in addition to Objective-C and C code. Use this extension only if you actually refer to C++ classes or features from your Objective-C code. |
When you want to include header files in your source code, use a #import directive, which is like C’s #include directive, except that it makes sure that the same file is never included more than once.
Figure 1 shows the syntax for declaring a class called MyClass, which inherits from the base (or root) class, NSObject. (A root class is one that all other classes directly or indirectly inherit from.) The class declaration begins with the @interfacecompiler directive and ends with the @end directive. Following the class name (and separated from it by a colon) is the name of the parent class. In Objective-C, a class can have only one parent. The instance variables of the class (sometimes referred to as ivars, and in some other languages called member variables) are declared in a code block that is delineated by braces ({ and }). Declarations of instance variables are optional. Following the instance variable block is the list of properties (not shown) and methods declared by the class. A semicolon character marks the end of each instance variable and method declaration.
Figure 1 A class declaration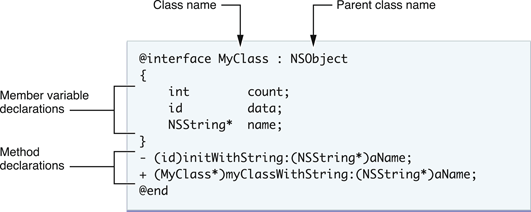
The syntax for a class implementation is similar. It begins with the @implementation compiler directive (followed by the name of the class) and ends with the @end directive. Method implementations go in between. An implementation should always import its interface file as one of the first lines of code.
#import "MyClass.h" |
@implementation MyClass |
- (id)initWithString:(NSString *)aName |
{
|
// code goes here
|
} |
+ (MyClass *)myClassWithString:(NSString *)aName |
{
|
// code goes here
|
} |
@end |
As mentioned earlier, Objective-C supports dynamic typing for variables containing objects, but it also supports static typing. Statically typed variables include the class name in the variable type declaration. Dynamically typed variables use the type id for the object instead. You find dynamically typed variables used in certain situations. For example, a collection object such as an array (where the exact types of the contained objects may be unknown) might use dynamically typed variables. Such variables provide tremendous flexibility and allow for much greater dynamism in Objective-C programs.
This example shows statically and dynamically typed variable declarations:
MyClass *myObject1; // Static typing |
id myObject2; // Dynamic typing |
NSString *userName; // From Your First iOS App (static typing) |
Notice the * in the first declaration. In Objective-C, object references must always be pointers. If this requirement doesn’t make complete sense to you, don’t worry—you don’t have to be an expert with pointers to be able to start programming with Objective-C. You just have to remember to put the * in front of the variable names for statically typed object declarations. The id type implies a pointer.
Methods and Messaging
If you’re new to object-oriented programming, it might help to think of a method as a function that is scoped to a specific object. By sending a message to—or messaging—an object, you call a method of that object. There are two kinds of methods in Objective-C: instance methods and class methods.
-
An instance method is a method whose execution is scoped to a particular instance of the class. In other words, before you call an instance method, you must first create an instance of the class. Instance methods are the most common type of method.
-
A class method is a method whose execution is scoped to the method’s class. It does not require an instance of an object to be the receiver of a message.
The declaration of a method consists of the method type identifier, a return type, one or more signature keywords, and the parameter type and name information. Here’s the declaration of the insertObject:atIndex: instance method.
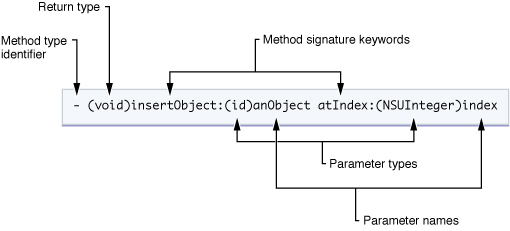
For instance methods, the declaration is preceded by a minus (-) sign; for class methods, the corresponding indicator is a plus sign (+). “Class Methods”, below, describes class methods in greater detail.
A method’s actual name (insertObject:atIndex:) is a concatenation of all of the signature keywords, including colon characters. The colon characters declare the presence of a parameter. In the above example, the method takes two parameters. If a method has no parameters, you omit the colon after the first (and only) signature keyword.
When you want to call a method, you do so by sending a message to the object that implements the method—or, in other words, messaging that object. (Although the phrase "sending a message” is commonly used as a synonym for “calling a method,” the Objective-C runtime does the actual sending.) A message is the method name along with the parameter information the method needs (properly conforming to type). All messages you send to an object are dispatched dynamically, thus facilitating the polymorphic behavior of Objective-C classes. (Polymorphism refers to the ability of different types of objects to respond to the same message.) Sometimes the method invoked is implemented by a superclass of the class of the object receiving the message.
To dispatch a message, the runtime requires a message expression. A message expression encloses with brackets ([ and]) the message itself (along with any required parameters) and, just inside the leftmost bracket, the object receiving the message. For example, to send the insertObject:atIndex: message to an object held by the myArray variable, you would use the following syntax:
[myArray insertObject:anObject atIndex:0]; |
To avoid declaring numerous local variables to store temporary results, Objective-C lets you nest message expressions. The return value from each nested expression is used as a parameter, or as the receiving object, of another message. For example, you could replace any of the variables used in the previous example with messages to retrieve the values. Thus, if you had another object called myAppObject that had methods for accessing the array object and the object to insert into the array, you could write the preceding example to look something like the following:
[[myAppObject theArray] insertObject:[myAppObject objectToInsert] atIndex:0]; |
Objective-C also provides a dot syntax for invoking accessor methods. Accessor methods get and set the state of an object, and thus are key to encapsulation, which is an important feature of all objects. Objects encapsulate, or hide, their state and present an interface common to all instances for accessing that state. Using dot syntax, you could rewrite the previous example as:
[myAppObject.theArray insertObject:myAppObject.objectToInsert atIndex:0]; |
You can also use dot syntax for assignment:
myAppObject.theArray = aNewArray; |
This syntax is simply a different way to write [myAppObject setTheArray:aNewArray];.
You have used dot syntax already for assigning to a variable in Your First iOS App:
self.userName = self.textField.text; |
“Declared Properties and Accessor Methods,” below, describes accessor methods in greater detail.
Class Methods
Although the preceding examples sent messages to an instance of a class, you can also send messages to the class itself. (A class is an object of type Class created by the runtime.) When messaging a class, the method you specify must be defined as a class method instead of an instance method. Class methods are a feature similar to static class methods in C++.
You often use class methods as factory methods to create new instances of the class or for accessing some piece of shared information associated with the class. The syntax for a class method declaration is identical to that of an instance method except that you use a plus (+) sign instead of a minus sign for the method type identifier.
The following example illustrates how you use a class method as a factory method for a class. In this case, the arraymethod is a class method on the NSArray class—and inherited by NSMutableArray—that allocates and initializes a new instance of the class and returns it to your code.
NSMutableArray *myArray = nil; // nil is essentially the same as NULL |
// Create a new array and assign it to the myArray variable. |
myArray = [NSMutableArray array]; |
Declared Properties and Accessor Methods
A property in the general sense is an item of state encapsulated by an object. It is either an attribute—such as a name or a color—or a relationship to one or more other objects. The class of an object defines an interface that enables users of its objects to get and set the values of encapsulated properties. The methods that perform this function are called accessor methods.
There are two types of accessor methods, and each method must conform to a naming convention. A “getter” accessor method, which returns the value of a property, has the same name as the property. A "setter” accessor method, which sets a new value for a property, has the form setPropertyName:, where the first letter of the property name is capitalized. Properly named accessor methods are a critical element of several technologies of the Objective-C frameworks.
Objective-C offers declared properties as a notational convenience for the declaration and sometimes the implementation of accessor methods. In Your First iOS App you declared the userName property:
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *userName; |
Declared properties eliminate the need to implement a getter and setter method for each property exposed in the class. Instead, you specify the behavior you want using the property declaration and then ask the compiler to synthesize—or, create—actual getter and setter methods based on that declaration. Declared properties reduce the amount of boilerplate code you have to write and, as a result, make your code much cleaner and less error prone.
You include property declarations with the method declarations in your class interface. The basic declaration uses the@property compiler directive, followed by the type information and name of the property. You can also configure the property with custom options, which define how the accessor methods behave, whether the property is a weak reference, and whether it is read-only. The options are in parentheses following the @property directive.
The following lines of code illustrate a few more property declarations:
@property BOOL flag; // Default is to simply assign value |
@property (copy) NSString *nameObject; // Copy the object during assignment. |
@property (readonly) UIView *rootView; // Declare only a getter method. |
In your class implementation, you can use the @synthesize compiler directive to ask the compiler to generate the accessor methods according to the specification in the declaration:
@synthesize flag; |
@synthesize nameObject; |
@synthesize rootView; |
You can combine the @synthesize statements in a single line if you want:
@synthesize flag, nameObject, rootView; |
In a @synthesize directive you can also instruct the compiler to add a corresponding instance variable to your class definition. To add an instance variable, after the property name, specify an equal sign and the name you want for the instance variable:
@synthesize nameObject=_nameObject; |
Blocks
Blocks are objects that encapsulate a unit of work—or, in less abstract terms, a segment of code—that can be executed at any time. They are essentially portable and anonymous functions that one can pass in as parameters of methods and functions or that can be returned from methods and functions. Blocks themselves have a typed parameter list and may have an inferred or a declared return type. You can also assign a block to a variable and then call it just as you would a function.
The caret symbol (^) is used as a syntactic marker for blocks. There are other, familiar syntactic conventions for parameters, return values, and body of the block (that is, the executed code). The following figure explicates the syntax, specifically when assigning a block to a variable.
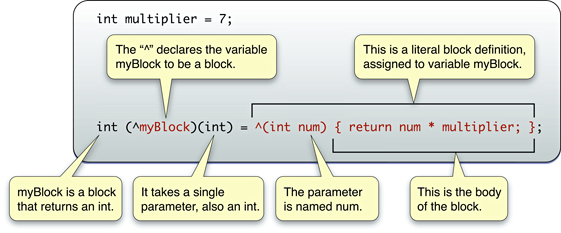
You can then call the block variable as if it were a function:
int result = myBlock(4); // result is 28 |
A block shares data in the local lexical scope. This characteristic of blocks is useful because if you implement a method and that method defines a block, the block has access to the local variables and parameters of the method (including stack variables) as well as to functions and global variables, including instance variables. This access is read-only, but if a variable is declared with the __block modifier, its value can be changed within the block. Even after the method or function enclosing a block has returned and its local scope is destroyed, the local variables persist as part of the block object as long as there is a reference to the block.
As method or function parameters, blocks can serve as a callback. When invoked, the method or function performs some work and, at the appropriate moments, calls back to the invoking code—via the block—to request additional information or to obtain program-specific behavior from it. Blocks enable the caller to provide the callback code at the point of invocation. Instead of packaging the required data in a “context” structure, blocks capture data from the same lexical scope as the host method or function. Because the block code does not have to be implemented in a separate method or function, your implementation code can be simpler and easier to understand.
Objective-C frameworks have many methods with block parameters. For example, the UIKit framework declares the following class method, which has two parameters that take blocks:
+ (void)animateWithDuration:(NSTimeInterval)duration delay:(NSTimeInterval)delay options:(UIViewAnimationOptions)options animations:(void (^)(void))animations completion:(void (^)(BOOL finished))completion; |
This method enables you to animate a view. The first block parameter is for specifying the animation; the second block parameter is for completing a task after the animation completes. In the following example, the first block simply sets the view’s ending alpha property to zero (making it transparent). The second block removes the view entirely.
[UIView animateWithDuration:0.2 animations:^{
|
view.alpha = 0.0;
|
} completion: ^(BOOL finished) {
|
if (finished == YES)
|
[view removeFromSuperview];
|
}]; |
Protocols and Categories
A protocol declares methods that can be implemented by any class, even if those classes implementing the protocol don’t have a common superclass. Protocol methods define behavior that is independent of any particular class. Protocols simply define an interface that other classes are responsible for implementing. When your class implements the methods of a protocol, your class is said to conform to that protocol.
From a practical perspective, a protocol defines a list of methods that establishes a contract between objects without requiring them to be instances of any specific class. This contract enables communication between those objects. One object wants to tell another object about the events it’s encountering, or perhaps it wants to ask for advice about those events.
The UIApplication class implements the required behavior of an application. Instead of forcing you to subclassUIApplication to receive simple notifications about the current state of the application, the UIApplication class delivers those notifications by calling specific methods of its assigned delegate object. An object that implements the methods of the UIApplicationDelegate protocol can receive those notifications and provide an appropriate response.
You specify in the interface block that your class conforms to, or adopts, a protocol by putting the name of the protocol in angle brackets (<...>) after the name of the class from which it inherits. You indicated adoption of theUITextFieldDelegate protocol in Your First iOS App:
@interface HelloWorldViewController : UIViewController <UITextFieldDelegate> {
|
} |
@end |
You do not have to declare the protocol methods you implement.
The declaration of a protocol looks similar to that of a class interface, with the exceptions that protocols do not have a parent class and they do not define instance variables (although they can declare properties). The following example shows a simple protocol declaration with one method:
@protocol MyProtocol |
- (void)myProtocolMethod; |
@end |
For many delegate protocols, adopting a protocol is simply a matter of implementing the methods defined by that protocol. There are some protocols that require you to state explicitly that you support the protocol, and protocols can specify both required and optional methods.
When you begin exploring the header files of the Objective-C frameworks, you’ll soon encounter a line similar to this one:
@interface NSDate (NSDateCreation) |
This line declares a category through the syntactical convention of enclosing the name of the category in parentheses. Acategory is a feature of the Objective-C language that enables you to extend the interface of a class without having to subclass it. The methods in the category become part of the class type (within the scope of your program) and are inherited by all the class’s subclasses. You can send a message to any instance of the class (or its subclasses) to invoke a method defined in the category.
You can use categories as a means for grouping related method declarations within a header file. You can even put different category declarations in different header files. The Cocoa Touch and Cocoa frameworks use these techniques throughout their header files for clarity. You can also use anonymous categories (which have no text between the parentheses) to hide instance variables in the private implementation file.
Defined Types and Coding Strategies
Objective-C has several terms that you should not use as the names of variables because they are reserved for special purposes. Some of these terms are compiler directives that are prefixed with at-signs (for example, @interface and @end). Other reserved terms are defined types and the literals that go with those types. Objective-C uses a number of defined types and literals that you won’t find in ANSI C. In some cases, these types and literals replace their ANSI C counterparts. The following table describes a few of the important ones, including the allowable literals for each type.
|
Type |
Description and literal |
|---|---|
|
|
The dynamic object type. The negative literal for both dynamically and statically typed objects is |
|
|
The dynamic class type. Its negative literal is |
|
|
The data type ( |
|
|
A Boolean type. The literal values are |
You often use these defined types and literals in error-checking and control-flow code. In your program’s control-flow statements, you can test the appropriate literal to determine how to proceed. For example:
NSDate *dateOfHire = [employee dateOfHire]; |
if (dateOfHire != nil) {
|
// handle this case
|
} |
To paraphrase this code, if the object representing the date of hire is not nil—in other words, it is a valid object—then the logic proceeds in a certain direction. Here’s a shorthand way of doing the same branching:
NSDate *dateOfHire = [employee dateOfHire]; |
if (dateOfHire) {
|
// handle this case
|
} |
You can even reduce these lines of code further (assuming you don’t need a reference to the dateOfHire object):
if ([employee dateOfHire]) {
|
// handle this case
|
} |
You handle Boolean values in much the same way. In this example, the isEqual: method returns a Boolean value:
BOOL equal = [objectA isEqual:objectB]; |
if (equal == YES) {
|
// handle this case
|
} |
You can shorten this code in the same way you can for the code that tests for the absence or presence of nil.
In Objective-C, you can send a message to nil with no ill effects. Indeed there is no effect at all, except that the runtime returns nil if the method is supposed to return an object. Return values from messages sent to nil are guaranteed to work as long as what is returned is typed as an object.
Two other important reserved terms in Objective-C are self and super. The first term, self, is a local variable that you can use within a message implementation to refer to the current object; it is equivalent to this in C++. You can substitute the reserved word super for self, but only as the receiver in a message expression. If you send a message to self, the runtime first looks for the method implementation in the current object’s class; if it can’t find the method there, it looks for it in its superclass (and so on). If you send a message to super, the runtime first looks for the method implementation in the superclass.
The primary uses of both self and super have to do with sending messages. You send a message to self when the method to invoke is implemented by the class of self—for example:
[self doSomeWork]; |
self is also used in dot notation to invoke the accessor method synthesized by a declared property, for example:
NSString *theName = self.name; |
You often send messages to super in overrides (that is, reimplementations) of methods inherited from a superclass. In this case, the method invoked has the same signature as the method overridden.




